I. Process Flow Overview
Granite sand production sites typically employ a multi-stage crushing and screening process. Through scientifically optimized equipment configuration and process parameter control, this approach achieves efficient, high-quality manufactured sand production. The process encompasses critical stages including primary crushing, secondary/tertiary crushing, sand shaping, washing, and dewatering. Each stage is seamlessly integrated to collectively ensure the quality of the finished sand.
II. Specific Process Steps
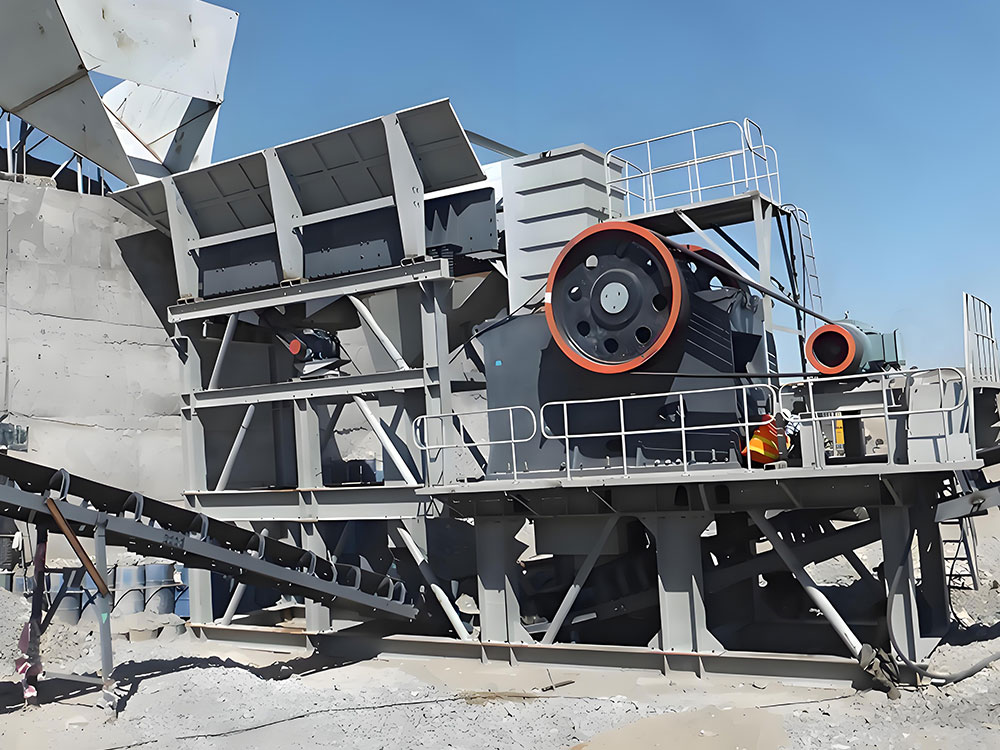
1. Primary Crushing Stage
Raw Material Handling: Large granite blocks (≤1500mm) enter the production line first. These bulk materials are placed on a vibrating feeder, which uniformly vibrates to deliver granite at a steady rate and flow into the jaw crusher. For example, in a granite sand plant processing 2000 tons per day, the vibrating feeder uniformly conveys approximately 250 tons of granite raw material per hour.
Coarse Crushing Operation: The jaw crusher employs the squeezing action between the moving and fixed jaws to perform coarse crushing on the large granite blocks. After coarse crushing, the output consists of coarse aggregate with a particle size ≤300mm. In actual production, the jaw crusher's processing capacity is closely related to the hardness and particle size of the raw material. Generally, for granite of moderate hardness, the jaw crusher can process 300–500 tons of raw material per hour, producing approximately 200–350 tons of coarse aggregate.
Precautions: Strict control of feed size is essential during this stage. Excessively large feed sizes exceeding the jaw crusher's rated capacity will reduce the efficiency of subsequent equipment. For instance, when feed size exceeds 1500mm, the crusher's efficiency drops by approximately 20%, while simultaneously increasing equipment wear and shortening its service life.
2. Medium and Fine Crushing Stage
Material Conveyance and Crushing: Material from coarse crushing is transported via belt conveyors to cone crushers for medium and fine crushing. Employing the layer compression crushing principle, cone crushers reduce material to ≤60mm through conical rotation and compression. In a medium-sized granite sand plant, the cone crusher processes 200–300 tons of coarse crushed material per hour, yielding approximately 180–270 tons of medium-fine crushed product.
Closed-Circuit Design: To ensure particle size compliance, this stage incorporates a vibrating screen for closed-circuit operation. The vibrating screen separates the crushed material: qualified particles proceed to the next process, while oversized particles are returned via a belt conveyor to the cone crusher for re-crushing. For example, with a 60mm screen aperture, approximately 10–15% of material is returned due to oversize.
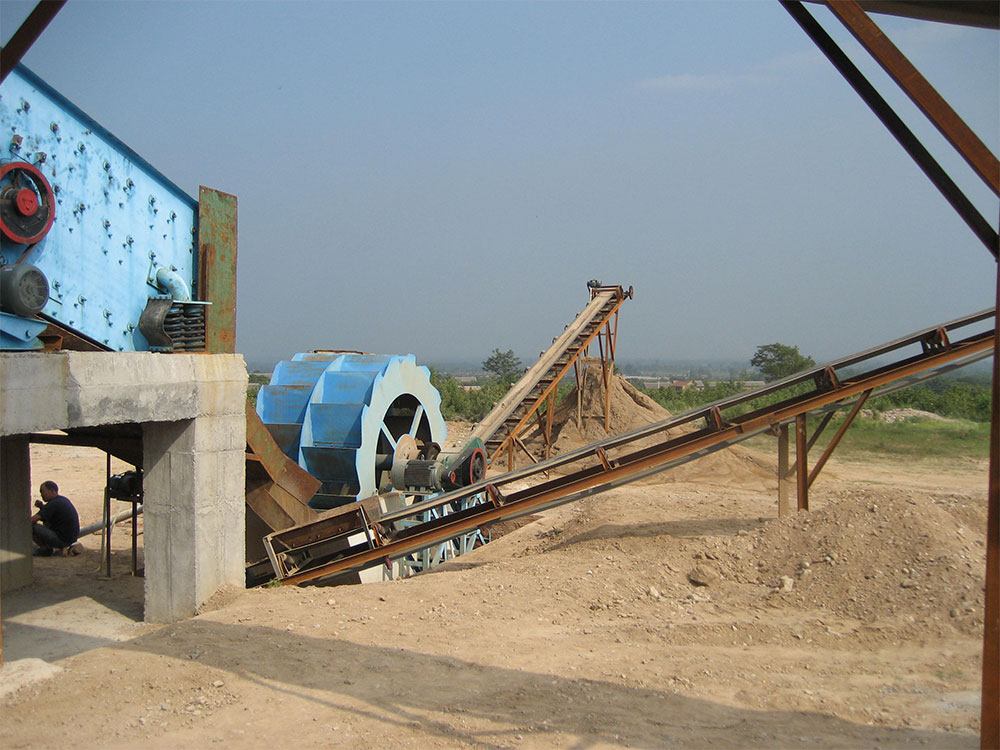
3. Sand Making and Shaping
Sand Making Process: Medium-fine crushed material enters the vertical shaft impact sand maker, where it undergoes crushing via either the “stone-on-stone” or “stone-on-iron” mode. The “stone-on-stone” mode is suitable for high-hardness granite, achieving fragmentation through mutual impact between particles. The “stone-on-iron” mode is ideal for applications requiring superior particle shape, utilizing the collision between material and metal liners to refine particle form. After processing, the material is produced as 0–5 mm manufactured sand. In a large-scale granite sand plant, the vertical shaft impact crusher can process 150–200 tons of medium-fine crushed material per hour, yielding approximately 130–180 tons of manufactured sand.
Sand Gradation Optimization: High-pressure roller mills further optimize sand gradation and enhance the fineness modulus. Through high-pressure compression, these mills achieve a more uniform particle size distribution, increasing the fineness modulus by 0.1–0.2. For instance, after processing by the high-pressure roller mill, the fineness modulus of manufactured sand can increase from 2.8 to approximately 3.0, better meeting construction engineering requirements for sand particle gradation.
4. Washing and Dewatering
Wet Process: For sand with high silt content, washing by a sand washer is required. The sand washer uses water flow to remove soil, impurities, and other contaminants from the sand. The washed sand then undergoes dewatering via a dewatering screen, yielding premium sand with a moisture content ≤15%. In a sand production plant processing 1,000 tons of premium sand daily, the sand washer can handle 120–150 tons of high-silt-content sand per hour, while the dewatering screen reduces moisture content from 30%–40% to below 15%.
Dry Process: The dry process replaces water washing with dust removal equipment. Utilizing a fan, this equipment extracts dust from the sand to achieve purification. The dry process is suitable for regions with scarce water resources, simultaneously reducing wastewater discharge and alleviating environmental pressure.
III. Key Equipment Configuration
1. Core Equipment
Jaw Crusher (Primary Crushing): The jaw crusher serves as the core equipment for primary crushing, offering advantages such as simple structure, reliable operation, and high crushing ratio. Its processing capacity varies by model, with common jaw crushers handling 100–1000 tons of raw material per hour.
Cone Crusher (Medium/Fine Crushing): Cone crushers are suitable for medium and fine crushing stages, characterized by high crushing efficiency and uniform product particle size. Their processing capacity generally ranges from 100 to 800 tons per hour, with different models selectable based on production requirements.
Vertical Shaft Impact Crusher (Shaping): The vertical shaft impact crusher is the key equipment for the sand shaping stage, producing manufactured sand with excellent particle shape and reasonable gradation. Its processing capacity typically ranges from 50 to 500 tons per hour, selectable based on raw material hardness and output requirements.
2. Auxiliary Systems
Vibrating Screen: Vibrating screens are used to classify crushed materials, separating qualified products from unqualified ones. Common types include circular vibrating screens and linear vibrating screens, achieving screening efficiencies exceeding 90%.
Belt Conveyor: Belt conveyors serve as the primary material handling equipment, enabling continuous and stable transportation of materials between processes. Their conveying capacity varies based on belt width and speed, with common models handling 50–2000 tons per hour.
Dust Removal/Sand Washing Equipment: Dust removal systems eliminate particulate matter from sand in dry processes, while sand washing equipment cleans sand in wet processes. Dust removal efficiency exceeds 95%, and sand washing recovery rates surpass 90%.
3. Specialized Processes
Hard Granite Crushing: For hard granite, a three-stage crushing process of “jaw crusher + cone crusher + sand maker” is recommended. This process maximizes the strengths of each equipment, enhancing crushing efficiency and product quality. For example, when crushing granite with a hardness of 120–140 MPa, the three-stage process increases finished sand output by 15%–20% while reducing needle and flake particle content by 20%–30%.
Soft Rock Crushing: For soft rock, the crushing process can be simplified using a two-stage crushing process: “jaw crusher + sand maker.” Soft rock has lower hardness and is easier to crush. The two-stage process meets production requirements while reducing equipment investment and operating costs.
IV. Key Quality Control Points
1. Control Crushing Ratio
Coarse Crushing Ratio: The coarse crushing ratio is recommended to be controlled between 4 and 6. A reasonable coarse crushing ratio ensures the crushing efficiency of the jaw crusher while providing suitable feed particle size for subsequent medium and fine crushing stages. For example, when the coarse crushing ratio is 5, the jaw crusher achieves optimal processing capacity, and the operation of subsequent equipment remains relatively stable.
Medium and Fine Crushing Ratio: The medium and fine crushing ratio is recommended to be controlled between 3 and 4. An appropriate medium-fine crushing ratio reduces the production of needle-like and flake-like particles, improving the quality of finished sand. Research indicates that when the medium-fine crushing ratio is 3.5, the content of needle-like and flake-like particles can be reduced to below 10%.
2. Feed Size Optimization
Medium-Fine Crushing Feed: Controlling the medium-fine crushing feed size at ≤50mm can reduce needle-like and flake-like particle content by 38%. In actual production, installing appropriate screening equipment between the primary crusher and cone crusher ensures feed size compliance. For instance, at a granite sand plant, optimizing screen mesh size to control medium-fine crushing feed ≤50mm reduced needle-flake particles in finished sand from 18% to 11%.
3. Closed-Circuit Design
Screen Recirculation: Returning oversized material for re-crushing enhances yield. Closed-circuit design recirculates oversized particles for reprocessing, ensuring thorough crushing and shaping to improve product compliance. For instance, a sand plant producing 800 tons of finished sand daily achieved a yield increase from 85% to 92% after implementing closed-circuit design.
4. Finished Product Quality Standards
This process achieves over 90% output of finished sand below 5mm, meeting the sand standards for C30 and higher concrete. C30 and higher concrete imposes strict requirements on sand particle size, gradation, clay content, and other indicators. Through the aforementioned process flow and quality control measures, high-quality manufactured sand compliant with standards can be produced.