What is the Working Principle of an Impact Crusher?
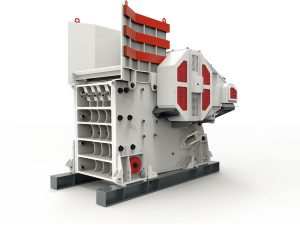
The impact crusher is a versatile crushing machine designed to reduce large materials into smaller, uniform-sized aggregates. At its core, the working principle of an impact crusher relies on high-speed impact forces to fracture materials. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how it operates:
1. Material Feeding: Raw material enters the crusher through a feed hopper and is directed toward a rapidly rotating rotor.
2. Acceleration by Rotor: The rotor, equipped with blow bars or hammers, accelerates the material to high speeds.
3. Impact and Fragmentation: The accelerated material collides with impact plates or aprons lining the crushing chamber, causing it to fracture.
4. Size Control: Adjustable aprons or grinding paths regulate the final product size by controlling the material’s trajectory and retention time in the chamber.
5. Output Screening: Crushed material exits through a discharge opening, often passing through a screening system to ensure uniformity.
This impact crushing mechanism excels at producing cubical-shaped aggregates, making it ideal for applications requiring precision and consistency.
Types of Impact Crushers: HSI vs. VSI
When exploring types of impact crushers, two primary categories dominate the market: Horizontal Shaft Impactors (HSI) and Vertical Shaft Impactors (VSI). Each type offers unique advantages depending on the application.
1. Horizontal Shaft Impact Crusher (HSI)
The HSI impact crusher features a horizontal rotor configuration and is widely used in primary, secondary, or tertiary crushing stages. Key characteristics include:
- Blow Bars: Replaceable wear parts that strike and fragment materials.
- Adjustable Aprons: Allow operators to fine-tune output size.
- High Reduction Ratios: Efficiently processes soft to medium-hard materials like limestone or recycled concrete.
HSI crushers are favored in quarrying, mining, and construction due to their versatility and cost-effectiveness.
2. Vertical Shaft Impact Crusher (VSI)
The VSI impact crusher employs a vertical rotor design, utilizing centrifugal force to propel material against stationary anvils or rock shelves. Notable features include:
- Rock-on-Rock vs. Rock-on-Iron: Configurations for shaping or grinding materials.
- Energy Efficiency: Optimized for producing finely graded sand and aggregates.
- Low Wear Costs: Ideal for abrasive materials like silica or granite.
VSIs are critical in producing high-quality manufactured sand for the construction and asphalt industries.
Applications of Impact Crushers Across Industries
Impact crushers serve diverse sectors owing to their adaptability and efficiency. Below are key application areas for this equipment:
1. Mining and Aggregate Production
- Primary Crushing: HSI crushers process large ore chunks into manageable sizes.
- Aggregate Shaping: VSIs refine crushed stone into premium-grade sand for concrete and road bases.
2. Construction and Demolition Recycling
- Concrete Recycling: Impact crushers break down demolished concrete into reusable aggregates.
- Asphalt Processing: HSI models efficiently reduce reclaimed asphalt pavement (RAP) for repaving projects.
3. Industrial Material Processing
- Glass and Ceramics: Delicate fragmentation without excessive fines.
- Coal and Chemicals: Crushing brittle materials to specific sizes for energy or manufacturing.
Technical Parameters of Impact Crushers
When selecting an impact crusher, understanding its technical specifications ensures optimal performance. Below are critical parameters to consider:
1. Rotor Speed and Power
- Rotor Diameter: Influences material acceleration (e.g., 800–1,500 mm for HSI models).
- Motor Power: Ranges from 75 kW for compact units to 600 kW for industrial-grade crushers.
2. Feed Size and Capacity
- Maximum Feed Size: Typically 200–800 mm, depending on crusher type.
- Throughput Capacity: Varies from 50 TPH (tonnes per hour) for small VSIs to 2,500 TPH for large HSI units.
3. Output Gradation
- Adjustable Settings: Apron gaps or rotor speeds control particle size distribution.
- Cubicity Index: Measures aggregate shape quality (≥90% for premium VSIs).
4. Wear Parts and Maintenance
- Blow Bar Lifespan: 150–500 hours, influenced by material abrasiveness.
- Easy Access Design: Reduces downtime during part replacement.
Advantages of Modern Impact Crusher Designs
Contemporary impact crusher technology integrates innovations to enhance productivity and sustainability:
1. Smart Automation Systems
- Remote Monitoring: Real-time tracking of rotor speed, wear levels, and throughput.
- Automated Adjustments: Self-optimizing aprons for consistent output quality.
2. Eco-Friendly Operation
- Reduced Dust Emissions: Sealed chambers and advanced filtration systems.
- Energy Recovery: Regenerative drives capture kinetic energy during deceleration.
3. Modular Components
-Quick-Change Wear Parts: Minimize downtime in high-intensity operations.
- Scalable Configurations: Adapt crushers to evolving production needs.
Choosing the Right Impact Crusher for Your Needs
Selecting between types of impact crushers hinges on material properties, desired output, and operational goals. Consider these factors:
1. Material Hardness and Abrasiveness
- HSI Crushers: Best for soft to medium-hard materials.
- VSI Crushers: Excel in processing abrasive or high-purity substances.
2. Desired Product Shape
- Cubical Aggregates: Opt for HSI or rock-on-rock VSI configurations.
- Fine Sand Production: Choose rock-on-iron VSI systems.
3. Production Scale
- Small to Medium Sites: Compact HSI units with lower capital costs.
- Large Quarries: High-capacity VSIs for continuous, high-volume output.
The impact crusher remains a cornerstone of material processing, combining robust engineering with operational flexibility. By understanding its working principle, exploring types of impact crushers, and evaluating technical parameters, industries can optimize crushing efficiency for applications ranging from mining to recycling. With advancements in automation and sustainability, modern impact crushers are poised to meet the evolving demands of global industries.